Quantum Phenomena
Two rapid communications analyzing the photoelectric effect and radioactive decay as well as an original article on quantum computing.
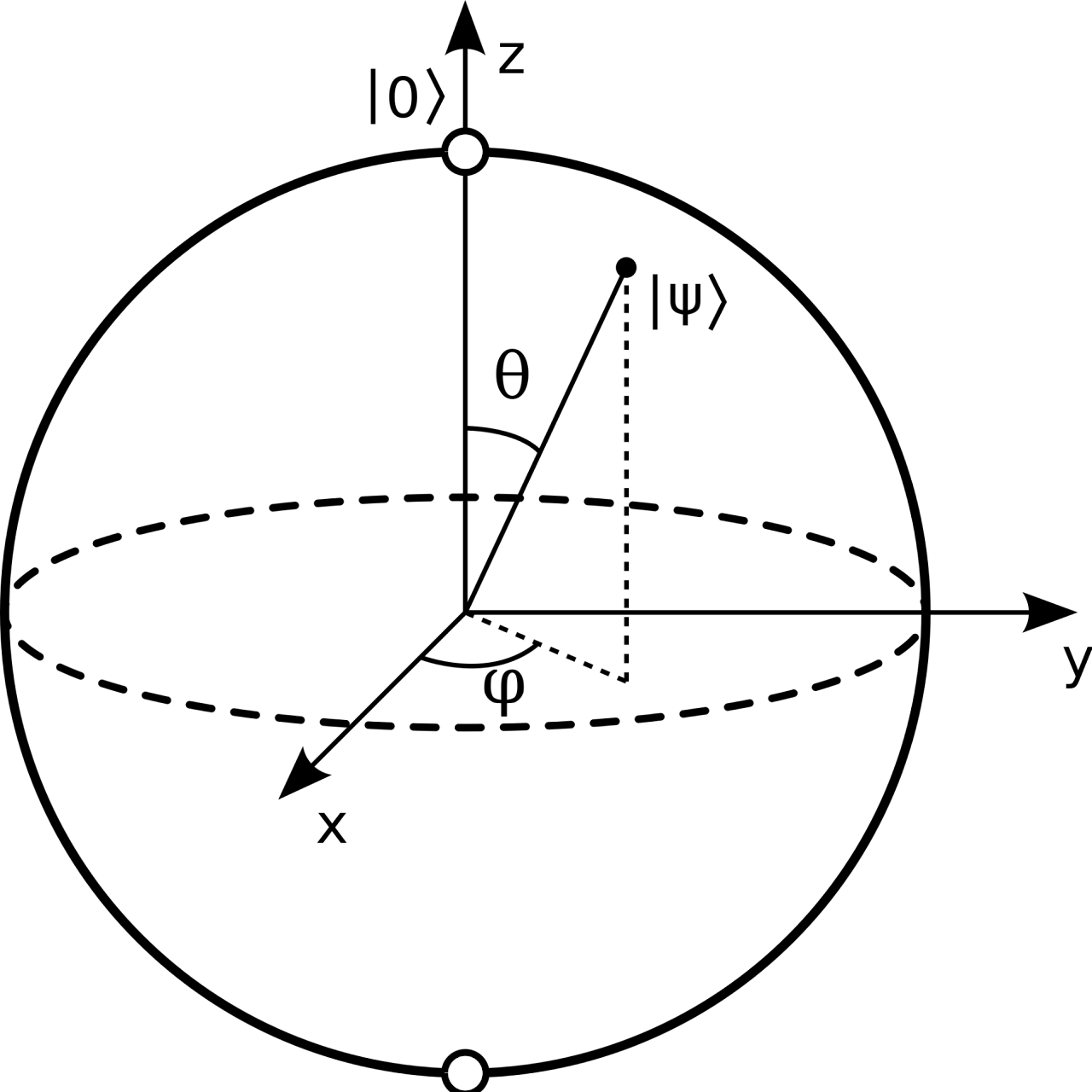
An undergraduate overview on quantum computing
Author: Carissa Kiehl
Abstract: This paper is a literature review on quantum computing. It presents a comprehensive overview of the history of quantum computing, including its origins in quantum mechanics. It also presents an overview on how quantum computing works, from qubits to quantum gates and circuits. Three subfields of quantum computing (quantum information science, quantum cryptography, and quantum machine learning) are discussed to provide more insight into the real-world applications of quantum computing. Lastly, the paper discusses the future of quantum computing and current research being done to further the field.
Lighting up the quantum world: a dive into the photoelectric effect and Planck’s constant
Author: Logan Dales
Abstract: The photoelectric effect caused classical physics and assumptions about energy to break down, resulting in the entire field of quantum physics to be created. In this report we use the photoelectric experiment set up to measure stopping voltages of different wavelengths of light in order to determine the value for Planck's universal constant from the slope of stopping voltage vs frequency plot. The importance of determining the value of a constant in different circumstances should never be squandered. Constants in physics are defined as fixed values and which have no uncertainty, so they must be true in any possible circumstance where they have an impact \cite{constant}. Even though there will be some uncertainty in the value we find, the accepted value falls close to the middle of our range which is a good result for the accuracy of the experimental setup.
Finding the range of beta decay using the changes in radiation magnitude from shielding and distance
Author: Kassia Schraufnagel
Abstract: The distance dependence of beta decay, a type of ionizing radiation, is measured using a Geiger counter. The decline in radiation magnitude as distance increases is measured to be a 1/r^2 relationship. During the experiment, a plastic sheet is used to determine the extent to which plastic shielding affects radiation magnitude. The experiment concludes that the plastic shielding has a large effect on the measured magnitude, but would not be an ideal material for shielding.